Eric A. Johnson, MS
Biography
Eric Johnson, MS, completed the University of Washington’s biostatistics master’s program in 2008. His thesis explored common theoretical problems involved with missing data. He quantified them, highlighting conditions leading to suboptimal performance, and provided new guidelines for using various multiple imputation techniques.
During his time at KPWHRI, Mr. Johnson has been involved with multiple projects involving direct intervention with the care-delivery system, observational studies and microsimulation modeling on colorectal and ovarian cancer, massage therapy, and estimating radiation exposure from medical imaging. His current responsibilities lie in research on obesity, opioids, and mental health.
Before earning his master’s degree, Mr. Johnson worked for four years as a research assistant on the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), performing statistical analyses, verifying incoming data, and developing a process for providing data sets to all MESA researchers. Later, he was a research statistician with the Department of Veteran Affairs (VA), serving as the primary analyst in an investigation of how well VA hospitals performed non-cardiac surgeries. Mr. Johnson assessed statistical models used by the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program—then devised, tested, and implemented improved models, reporting his findings to VA leadership.
Research interests and experience
-
Biostatistics
Multiple imputation; prediction models, working with large data
-
Health Systems
Implementing prediction models, and validating that they work as intended. Research into interventions that are financially feasible for health systems to widely implement
-
Cancer
-
Complementary & Integrative Health
-
Health Services & Economics
-
Obesity
-
Mental Health
Recent publications
Reid RJ, Johnson EA, Hsu C, Ehrlich K, Coleman K, Trescott C, Erikson M, Ross TR, Liss DT, Cromp D, Fishman PA. Spreading a medical home redesign: effects on emergency department use and hospital admissions. Ann Fam Med. 2013 May-Jun;11 Suppl 1:S19-26. doi: 10.1370/afm.1476. PubMed
Chubak J, Rutter CM, Kamineni A, Johnson EA, Stout NK, Weiss NS, Doria-Rose VP, Doubeni CA, Buist DS. Measurement in comparative effectiveness research. Am J Prev Med. 2013 May;44(5):513-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2013.01.006. PubMed
Doubeni CA, Weinmann S, Adams K, Kamineni A, Buist DS, Ash AS, Rutter CM, Doria-Rose VP, Corley DA, Greenlee RT, Chubak J, Williams A, Kroll-Desrosiers AR, Johnson E, Webster J, Richert-Boe K, Levin TR, Fletcher RH, Weiss NS. Screening colonoscopy and risk for incident late-stage colorectal cancer diagnosis in average-risk adults: a nested case-control study. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158(5 Pt 1):312-20. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-5-201303050-00003. PubMed
Fishman PA, Johnson EA, Coleman K, Larson EB, Hsu C, Ross TR, Liss D, Tufano J, Reid RJ. Impact on seniors of the patient-centered medical home: evidence from a pilot study. Gerontologist. 2012 Oct;52(5):703-11. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnr158. Epub 2012 Mar 15. PubMed
Smith-Bindman R, Miglioretti DL, Johnson E, Lee C, Feigelson HS, Flynn M, Greenlee RT, Kruger RL, Hornbrook MC, Roblin D, Solberg LI, Vanneman N, Weinmann S, Williams AE. Use of diagnostic imaging studies and associated radiation exposure for patients enrolled in large integrated health care systems, 1996-2010. JAMA. 2012;307(22):2400-9. PubMed
Hsu C, Coleman K, Ross TR, Johnson E, Fishman PA, Larson EB, Liss D, Trescott C, Reid RJ. Spreading a patient-centered medical home redesign: a case study. J Ambul Care Manage. 2012;35(2):99-108. PubMed
Rutter CM, Johnson E, Miglioretti DL, Mandelson MT, Inadomi J, Buist DS. Adverse events after screening and follow-up colonoscopy. Cancer Causes Control. 2012 Feb;23(2):289-96. Epub 2011 Nov 22. PubMed
Cherkin DC, Sherman KJ, Kahn J, Wellman R, Cook AJ, Johnson E, Erro JH, Delaney KM, Deyo RA. A comparison of the effects of 2 types of massage and usual care on chronic low back pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011 Jul 5;155(1):1-9. PubMed
Cook CR, Joo MJ, Anderson SM, Lee TA, Udris EM, Johnson EA, Au DH. The validity of using ICD-9 codes and pharmacy records to identify patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011 Feb 16;11:37. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-11-37. PubMed
Reinke LF, Slatore CG, Udris EM, Moss BR, Johnson EA, Au DH. The association of depression and preferences for life-sustaining treatments in veterans with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2011 Feb;41(2):402-11. Epub 2010 Dec 8. PubMed
Research

Study finds bariatric surgery linked to substantially lower risk of blood clots long-term
Largest study to date helps patients weigh risks and benefits of surgery.
New findings

Simpler models to identify suicide risk perform similarly to more complex ones
Models that are easier to explain, use could have better uptake in health care settings.
New findings

Research roundup on natural language processing and machine learning
Using doctor's notes to learn about drug reactions, dementia, and cannabis use.
New findings
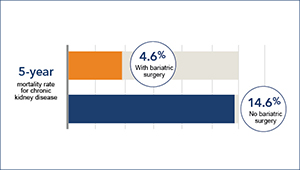
Is bariatric surgery helpful in chronic kidney disease?
David Arterburn and colleagues find that bariatric surgery is linked to lower death risk in persons with obesity and CKD.



