A simple solution to help catch cervical cancer early

Research finds that mailing HPV test kits directly to patients increases cervical cancer screening rates
Three years ago, the federal government set a series of targets to improve Americans’ overall health. Among the dozens of goals laid out in the plan, called Healthy People 2030, was a significant increase in the proportion of Americans who kept up to date with cervical cancer screening.
That, in turn, would enable more people to detect cervical cancer early, when it’s most treatable.
New research from the University of Washington and Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute (KPWHRI) found that the simplest solution may also be the most effective: mailing test kits directly to patients’ homes. In a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers report that mailing test kits significantly increased cervical cancer screening rates, both among people overdue for screening and those who had previously kept up to date.
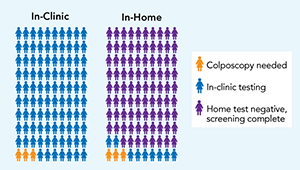
The home test kits detect the presence of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which causes most cervical cancers. And a negative home HPV test counts as a negative cervical cancer screening, allowing most people to avoid a clinic visit altogether. Currently, more than half of all cervical cancers diagnosed in the United States are in people who are overdue for screening or have never been screened. The team behind this study believes at-home testing can help close the gap.
“This is an alternative, patient-centered way to get people screened for cervical cancer, because patients tend to prefer testing at home and not having to come into the clinic,” said Rachel Winer, a UW professor of epidemiology and affiliate researcher at KPWHRI, who led the research. “This is a strategy that other countries are already using, and there’s overwhelming evidence that an HPV test on a patient-collected sample is similarly accurate to an HPV test on a sample collected by a clinician. So, there’s really no reason why this shouldn’t be available in the U.S.”
“Almost all cervical cancer can be prevented by identifying and removing precancers caused by high-risk HPV,” said Beverly Green, MD, MPH, a senior investigator at KPWHRI and co-lead of the study. “But fewer people are now getting screened, compared to 20 years ago. There are lots of reasons for this, including barriers to health insurance, lack of transportation or time, and embarrassment or discomfort. Home tests can help overcome some of those obstacles.”
In partnership with Kaiser Permanente Washington, researchers enrolled more than 31,000 patients between the ages of 30 and 64 who were either due or overdue for screening, or whose screening history was unknown. Patients were randomly sorted into 4 groups: One group had HPV test kits mailed directly to their homes, another received information on how to request a test kit, and another received an educational brochure on cervical cancer screening. The fourth group received only a standard reminder that participants were due for screening.
Over the next 6 months, 62% of people who were due for screening and 36% of people who were overdue were screened for cervical cancer after being directly mailed a kit. Those percentages fell to 48% and 19%, respectively, among patients who received only the educational brochure. Sending information on requesting a kit minimally increased screening.
The results, Winer said, indicate that health care systems should prioritize mailing HPV test kits directly to patients to maximize cervical cancer screening participation.
“We just think this should be an option for all patients,” Winer said. “It’s convenient, preferred by most patients, and an accurate way to screen for cervical cancer. So why not have it as an option?”
This study builds on previous research conducted by Winer and her colleagues, which found that mailing HPV test kits to under-screened patients increased screening rates, though most people remained untested. That study took place before the cervical cancer screening guidelines were updated to include HPV testing alone, so the test kit did not count as a regular screen.
Self-testing is already an option for other routine screenings, most notably for colorectal cancer. The most recent guidelines encourage home test kits as a primary screening option, suggesting that annual stool samples may be taken in place of a routine colonoscopy, which many patients find uncomfortable. Colorectal screening rates have risen steadily in recent years, and mortality and incidence rates for colorectal cancer have decreased by almost half in the last 3 decades.
There are still significant barriers to overcome before HPV self-sampling can become widely available, Winer said. Chief among them is approval by the Food and Drug Administration, which is expected to come in the next few months.
Once HPV self-sampling receives FDA approval for use as a cervical cancer screening tool, health care systems that want to implement self-screening need to procure test kits, review their policies, and educate both patients and providers. Algorithms used to track patients’ care also have to be updated. Health centers serving low-income and marginalized communities may not have the staff or financial resources to distribute test kits. Patients without a primary care physician may slip through the cracks.
“HPV self-sampling is a tool certainly designed to increase access and reduce disparities,” Winer said. “But sometimes when a new intervention is introduced, it can further widen disparities if there isn’t attention taken to how to best implement it, or how to specifically make sure that it reaches people who need it the most.”
Other authors on the study are John Lin, BA, research coordinator in the UW Department of Epidemiology; Melissa Anderson, MS, and Kristina Hansen, BA, from KPWHRI; Jasmin Tiro, PhD, and Hongyuan Gao, MS, from the University of Chicago; Richard Meenan, PhD, MPH, MBA, from the Kaiser Permanente Center for Health Research; Angela Sparks, MD, from UnitedHealthcare; and Diana Buist, PhD, MPH, of GRAIL LLC. The research was funded by the National Cancer Institute.
This has been adapted from a news story by Alden Woods at the University of Washington School of Medicine
Research to practice

Helping more patients get screened for cervical cancer
Research on at-home testing for HPV could improve cancer prevention and ease screening for patients.
Healthy Findings Blog

Cancer screening in the time of COVID-19
Dr. Diana Buist reflects on the challenges of providing screening during a pandemic — and finds reason for optimism.
cancer screening
Mailing home HPV test may offer alternative to Pap screen
Dr. Diana Buist and team reflect on HOME trial showing 50 percent screening boost in underscreened women.


